Blockchain, when to knock it's door?
Blockchain has been extremely popular in Tech arena these days. Companies are experimenting with it in many ways to fit it in their business solutions. Often, it has been difficult for most of us to identify the problem statements it was designed to solve or more specifically identify when actually one should consider using it.
I'll start this article with a reference to some of the lines in the original white-paper published on blockchain by Satoshi Nakamoto.
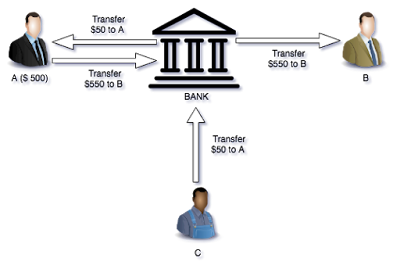
Suppose I (A) have only $ 500 in my bank account, but I want to buy iPhone X from (B) which costs $ 550. I ask my friend (C) to transfer $ 50 to my bank account so that I can make the purchase.
In this example for a successful purchase of iPhone by A, the Bank who is the central authority should ensure that the Transfer from C -> A should be processed before A -> B. If somehow the central authority is compromised then it can result in an invalid transaction as well. One can see that bank becomes a single point of failure here. Let's see how blockchain can solve this problem.
Using blockchain each of the transactions in above example will be a part of a ledger with each of A, B, C being users in the chain with a copy of the state of ledger after every successful transaction. Even if someone manipulates his copy and tries to make the chain dirty, it will not be possible as others with there copy of ledger can easily verify the corrupt transaction. See below diagrams which are simplified version of the actual blockchain ledger to make this concept clear.
Now since we have understood the concept, it will be good to understand when we should think about using blockchain as a solution.
I'll start this article with a reference to some of the lines in the original white-paper published on blockchain by Satoshi Nakamoto.
"What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party"The intention in the above white-paper though was to focus more on a currency (bitcoin), hence a reference to an electronic payment system is made. But at the heart of this white-paper was the idea to remove a central trust and to delegate the responsibility to the transacting parties. Let's try understanding it with an example -
Suppose I (A) have only $ 500 in my bank account, but I want to buy iPhone X from (B) which costs $ 550. I ask my friend (C) to transfer $ 50 to my bank account so that I can make the purchase.
In this example for a successful purchase of iPhone by A, the Bank who is the central authority should ensure that the Transfer from C -> A should be processed before A -> B. If somehow the central authority is compromised then it can result in an invalid transaction as well. One can see that bank becomes a single point of failure here. Let's see how blockchain can solve this problem.
Using blockchain each of the transactions in above example will be a part of a ledger with each of A, B, C being users in the chain with a copy of the state of ledger after every successful transaction. Even if someone manipulates his copy and tries to make the chain dirty, it will not be possible as others with there copy of ledger can easily verify the corrupt transaction. See below diagrams which are simplified version of the actual blockchain ledger to make this concept clear.
Now since we have understood the concept, it will be good to understand when we should think about using blockchain as a solution.
Use Cases
In general it can be used where transactions are involved. More specifically where the transaction history is important. Some of the examples are.- Financial Services - It can be either payment processing, transfer of money or related to lending of money.
- Trading - Be it share, energy or oil, trading is one of the best fits to use blockchain platform. It's so because during the lifecycle of either of these it goes through many parties who own them, hence for a new buyer tracking the historical transaction on a public ledger becomes extremely easy. It prevents thefts and frauds.
- Property - Since while purchasing a property it's very important to validate the owners which owned it in past, it becomes a perfect contender to be on the blockchain platform.
- Intellectual property and copyright - Again in the case of intellectual property it's important to track whether the current seller is a genuine owner or not. Since with blockchain a buyer can easily validate the history.
- Identity or individual record keeping




Comments
Post a Comment